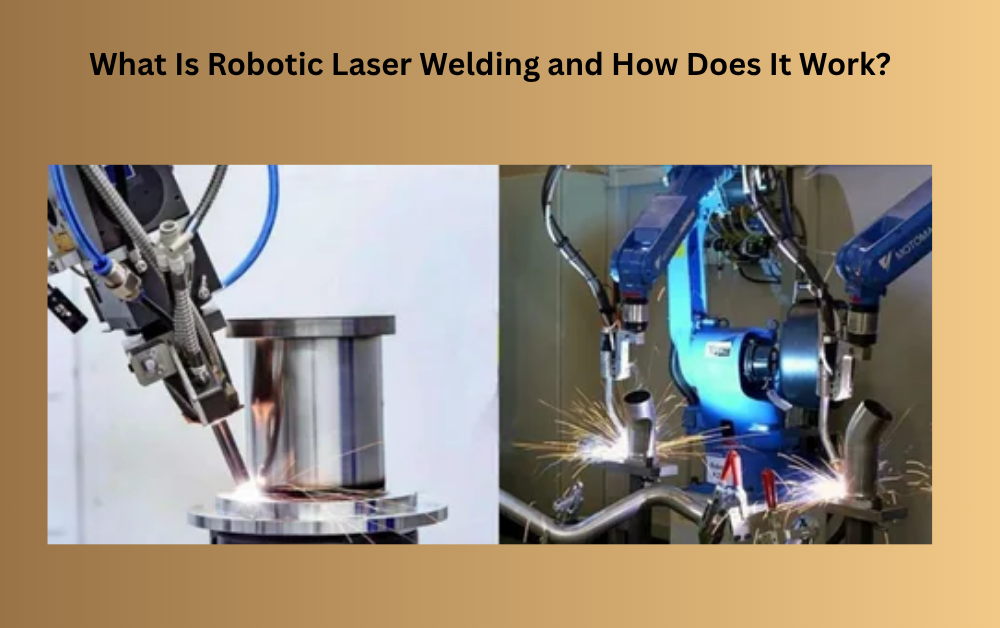
In today's fast-growing industrial world, automation is changing how we make and build things. One of the best examples of this progress is robotic laser welding . This modern technology combines the accuracy of lasers with the speed and consistency of robots to create strong, precise welds in a short amount of time.
From car factories to aerospace industries, robotic laser welding is helping companies make better products faster and with fewer errors. But what exactly is robotic laser welding, and how does it work? This article will explain everything in simple and easy-to-understand language — no technical jargon, just clear explanations that anyone can follow.
Understanding Robotic Laser Welding
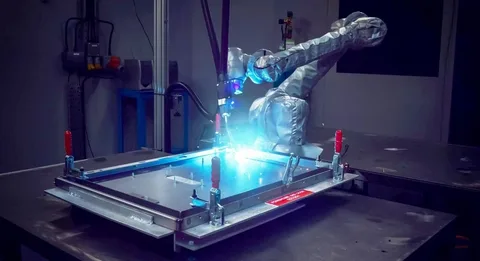
Robotic laser welding is an advanced welding process where a robot uses a powerful laser beam to join metal parts together. The laser acts as the heat source, melting the edges of the materials so they fuse into a strong joint when cooled.
In traditional welding, a person operates the equipment by hand. In robotic laser welding, a robot does this automatically with extreme precision. The robot's arm moves smoothly and accurately, guided by a computer program that follows specific patterns or paths.
Because the laser produces concentrated heat, it can melt metal quickly and create narrow, deep welds with very little distortion. This makes robotic laser welding ideal for industries that need clean, strong, and repeatable welds.
How Robotic Laser Welding Works
The process of robotic laser welding involves several steps and components that work together to make a perfect weld. Let’s understand them step by step.
Step 1: Preparation and Setup
Before welding starts, the materials to be joined are cleaned and positioned correctly. The robot’s system is programmed with exact instructions — such as where to weld, how deep, and at what speed.
This step ensures accuracy and reduces mistakes during the welding process.
Step 2: Laser Generation
The welding robot uses a laser source to create a focused beam of light energy. This beam is extremely hot and powerful, capable of melting metal in seconds. The laser’s energy is concentrated into a small spot, which makes the process efficient and fast.
Step 3: Welding Process
Once the laser beam touches the surface of the material, it instantly heats and melts the metal at the joint area. The robot moves the laser along the path that needs welding, and as it moves, the melted metal cools down and solidifies, forming a strong bond.
Because the robot’s movements are controlled by a computer, every weld is done with the same precision and consistency.
Step 4: Cooling and Inspection
After welding, the material cools naturally or with the help of air or gas. Once cooled, the joint becomes solid and strong.
Modern robotic systems often include sensors and cameras that inspect each weld automatically, checking for any errors or defects. This ensures high-quality results every time.
Components Used in Robotic Laser Welding
To understand how the process works, it helps to know about the main parts that make up a robotic laser welding system.
Robotic Arm
The robotic arm is the main part of the system. It moves the laser head precisely over the workpiece. The arm can move in multiple directions and angles, allowing it to reach complex areas easily.
Laser Source
The laser source is what generates the high-energy beam. Different types of lasers are used in welding, such as fiber lasers, CO₂ lasers, and diode lasers. Each has its own advantages depending on the material being welded.
Control System
The control system acts like the “brain” of the setup. It stores the welding program, controls the robot’s movements, and adjusts parameters like speed and laser power.
Cooling System
Since lasers generate a lot of heat, a cooling system is used to keep the equipment at a safe temperature and maintain efficiency.
Sensors and Cameras
Many robotic laser systems have built-in sensors and cameras to monitor the welding process. They detect errors, measure alignment, and ensure that the welds are perfect.
Types of Laser Welding Used in Robots
There are several types of laser welding techniques used in robotic systems, each suitable for different applications.
Conduction Laser Welding
In conduction laser welding, the laser beam heats the metal surface but does not penetrate deeply. This method is used for thin materials and when a smooth, shiny finish is needed — for example, in electronic parts or fine sheet metal work.
Keyhole Laser Welding
In this type, the laser creates a small “keyhole” in the material by melting it deeply. This allows the weld to go through thicker materials and create strong joints. Keyhole welding is commonly used in heavy industries like automotive and shipbuilding.
Hybrid Laser Welding
Hybrid laser welding combines laser welding with another process like arc welding. This method gives the best of both worlds — the deep penetration of laser welding and the stability of arc welding. It’s used in projects that need both speed and strength.
Advantages of Robotic Laser Welding
Robotic laser welding offers several benefits that make it far better than traditional manual welding. Let’s look at them one by one.
High Precision and Accuracy
Because the robot follows programmed instructions, every weld is done with perfect accuracy. This reduces human error and ensures consistent results. Even small parts can be welded with millimeter-level precision.
Speed and Efficiency
Laser welding is incredibly fast. When combined with robotic automation, production speed increases greatly. A robotic system can work for long hours without fatigue, making it ideal for mass production.
Strong and Clean Welds
The heat from the laser is focused in a very small area, which means the surrounding metal doesn’t get damaged. This produces clean, strong welds with minimal distortion or splatter.
Less Material Waste
Because of its precision, robotic laser welding minimizes waste. The exact amount of energy and filler is used, which saves materials and reduces costs.
Lower Maintenance and Operating Costs
Although the initial setup of robotic laser welding is expensive, it saves a lot of money in the long run. Robots require less manual labor and fewer repairs, and they work continuously without breaks.
Improved Safety
Since robots handle the welding process, workers don’t have to be exposed to intense heat, sparks, or fumes. This reduces workplace accidents and improves safety standards.
Applications of Robotic Laser Welding
Robotic laser welding is used in many industries because of its precision and reliability. Here are some of the main areas where it is applied:
Automotive Industry
Car manufacturers use robotic laser welding to assemble parts like doors, chassis, and exhaust systems. The process ensures uniform strength and perfect fitting for every vehicle.
Aerospace Industry
Aircraft components need extremely strong and lightweight joints. Robotic laser welding is ideal for this because it provides deep welds without adding much weight.
Electronics Manufacturing
In electronics, small and delicate parts are welded with lasers for clean, precise results. Robots handle these tasks with steady accuracy that human hands cannot achieve.
Construction and Machinery
Robotic laser welding is also used for building heavy machinery, tools, and industrial frames. It ensures the structures remain strong and stable even under pressure.
Medical Equipment
Medical devices like surgical tools and implants require tiny, clean welds that meet strict hygiene standards. Laser welding is perfect for this delicate work.
Challenges of Robotic Laser Welding
Even though robotic laser welding has many advantages, it also comes with some challenges.
-
High Initial Cost: Setting up a robotic laser welding system requires a big investment. However, the cost is balanced by long-term savings.
-
Technical Skill Required: Skilled technicians are needed to program and maintain the robots.
-
Material Limitations: Not all materials react the same way to laser heat, so choosing the right type of laser is important.
-
Regular Maintenance: To keep performance high, robotic systems need periodic checks and calibration.
Despite these challenges, most industries find that the long-term benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
The Future of Robotic Laser Welding
The future of robotic laser welding looks very bright. With new innovations in automation, artificial intelligence, and machine learning, welding robots are becoming smarter and more efficient.
In the future, we can expect systems that:
-
Adjust themselves automatically during welding
-
Detect and fix defects without human help
-
Use less energy while giving even better results
Robotic laser welding will continue to grow in industries like renewable energy, shipbuilding, and aerospace. As technology becomes more affordable, even small factories will start using it to improve productivity and quality.
Why Businesses Are Switching to Robotic Laser Welding
Companies across the world are moving toward robotic laser welding for several good reasons:
-
It speeds up production without sacrificing quality.
-
It reduces the risk of human error.
-
It helps meet growing demand for precise and durable products.
-
It improves workplace safety.
-
It allows 24/7 continuous production.
With all these benefits, it's no surprise that robotic laser welding is becoming a standard part of modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
Robotic laser welding is a perfect example of how technology is reshaping the future of manufacturing and construction. It combines the power of lasers with the intelligence of robots to create welds that are fast, clean, and incredibly precise.
From cars and airplanes to electronic devices and medical tools, this technology is making production faster, safer, and more reliable. While it may require a higher initial cost, the long-term advantages — including efficiency, safety, and durability — make it a smart investment for any industry.
As automation continues to evolve, robotic laser welding will play an even bigger role in building the strong, modern world we live in today.
For more insightful articles related to this topic, feel free to visit : turkhand.org